PLATE TECTONICS
Key Terms
Layers of the Earth
The crust is the outermost solid layer of the earth.
Tectonic plates are the huge rock sections that make up the earth's crust. They do move slowly, propelled by convection currents in the mantle.
The mantle is the layer directly below the crust, made of molten rock.
The core is the innermost layer of the earth.
Continental plates are made of lighter, less dense material than oceanic plates. They are lighter overall depsite being thicker, at 25-100km thick.
The earth's major landmasses are almost wholly on continental crust.
Oceanic plates are thinner than continental plates at just 5-10km, but are made of dense basalt and so are heavier.
They are, as their name implies, usually below the oceans. When oceanic crust moves into continental crust it is the oceanic crust that sinks due to its greater density.
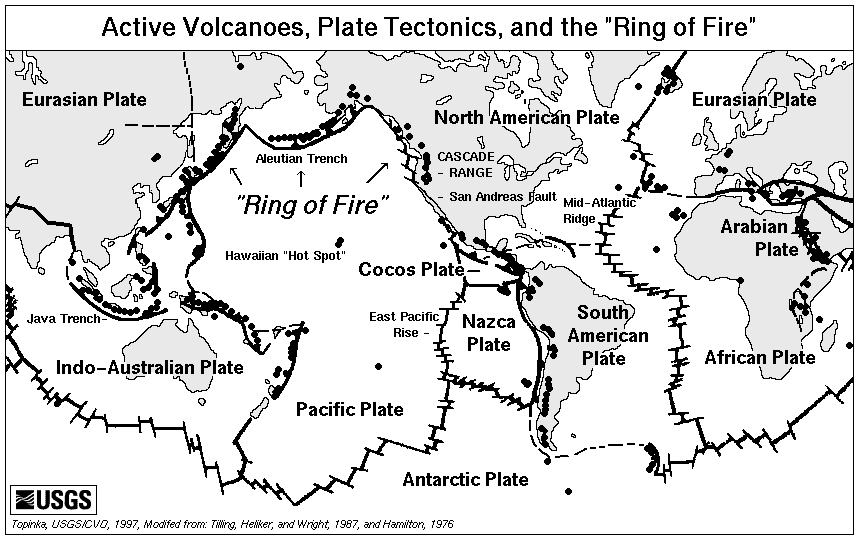
Plate Boundaries
A plate boundary is the line along which two plates meet.
A constructive boundary is where two plates are moving away from each other. Molten rock comes up along the gap, creating new crust in a long ridge. Volcanoes can be found on constructive boundaries.
Examples of constructive boundaries include the American/Eurasian plate rift down the Atlantic and through Iceland.
A destructive boundary is where an oceanic plate is moving under (or, technically being subducted under) a continental plate.
The dense oceanic crust moves down and is destroyed, but forces the continental curst upward. Volcanoes can be found on destructive boundaries.
Examples of destructive boundaries include the Pacific plate beung subducted under the South American Plate.
A conservative boundary is where two plates are moving alongside one another, either in opposite directions or in the same direction at different speeds. The best known
example of this is the San Andreas fault between the Pacific and North American plates. Volcanoes are never found at conservative boundaries.
A collision boundary is where two continental plates collide, pushing up huge ridges of rock. These never creat volcanoes, although they do build vast mountain ranges.
The Himalayas are on a collision boundary between the Eurasian and Indo-Australian plates.
More Information on Tectonics
Back
